Robust Design software - Robust Design is a new set of engineering and statistical tools to be used during the product realization process to ensure that products meet customer needs
|
Robust Design - Optimization
|
Robust Design - Parameter Design
|
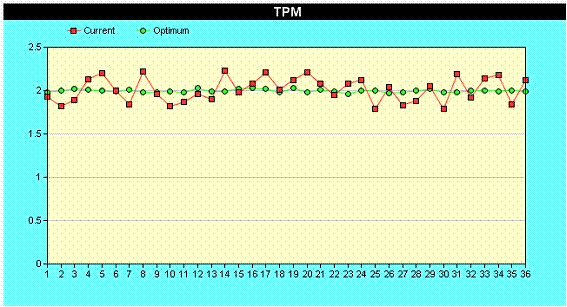
Computer Aided Parameter Design is an efficient simulation technique that allows known responses to be studied by modeling. Despite advances in computer technology, some simulation take a lot of computer effort or the enormous data output is not comprehensive. For the Wheatstone Bridge, the results above show how robust parameter setting can influence the stability of the mean despite variations in noise. The Computer Aided Parameter Design gives the user a systematic and consistent approach to solving engineering problems.
Computer Aided Parameter Design allows you to:
- Conduct Grid Search experiments
- Conduct Orthogonal Array experiments for
- Static Characteristics
- Dynamic Characteristics
|
|
|
|
Robust Design - Data Transformation
|
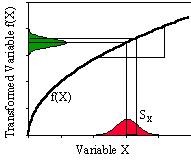 |
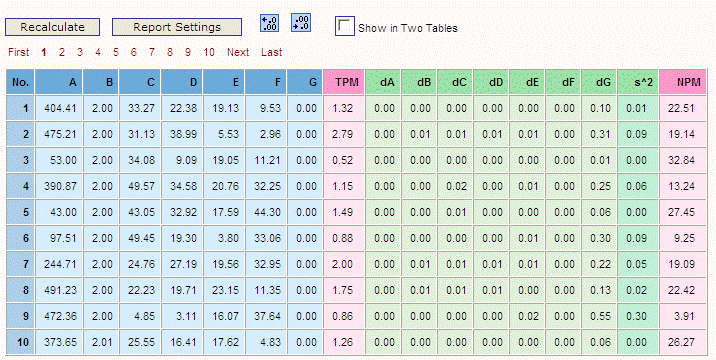
Data Transformation is an interesting area that reconciles Taguchi's ideas with that of classical Design of Experiments. Data Transformation is used to identify two metrics (TPM, target performance measure and NPM, noise performance measure) so that a 2-Step optimization process can be used. The 2-Step optimization is based on minimizing variability independent of the mean. The NPM can then be used to reduce variability and the TPM can be used to adjust to target. NPMs are a richer class of measures which Taguchi calls the signal-to-noise (SN) ratio. Data Transformation allows you to:
- Perform the Lambda Technique
- Perform the Beta Technique
- Study the Lambda Technique and Beta Technique to
- Identify an appropriate TPM
- Identify an appropriate NPM
- Understand the weaknesses of Taguchi's signal-to-noise ratios
|
|
|
|
Robust Design - Tolerance Design
|
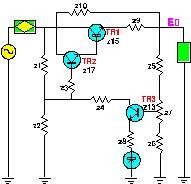 |
Tolerance Design is used to achieve higher quality by reducing the intrinsic variability of components for known responses. It is often difficult to identify which component in an assembly causes the highest variability. Knowing this is helpful in upgrading only that component to keep costs to a minimum.
Computer Aided Tolerance Design allows you to:
- Identify which component causes the greatest variation
- Select which components to upgrade
- Evaluate the impact of cost on upgrading components
|
|
|
|
Robust Design - Successive Approximation
|
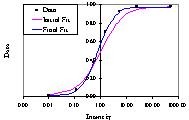 |
Successive Approximation is an iterative method which minimizes the residual sum of square in an analysis of variance. The method is particularly useful to fit non-linear functions and can be used to improve empirical curve fitting where the formula is changed to provide the best fit. Successive Approximation allows you to:
- Use different empirical functions
- Modify functions to improve empirical curve fitting
|
|
|
|
Robust Design - Minute Accumulation Analysis
|
 |
Minute Accumulation Analysis is an interesting approach to reliability studies. Here is a method that can be used to improve reliability using a parameter design approach. Minute Accumulation Analysis allows you to:
- Conduct an objective reliability study
- Determine optimum factors for reliability
- Calculate the expected improvement
|
|
|
|
Robust Design - Monte Carlo Simulation
|
Monte Carlo Simulation is an interesting approach to conducting experiments. This method can be used to conduct experiments using random variables for factors. iCT-M allows free number, stepped and orthogonal array subsets of simulations. Monte Carlo Simulation allows you to:
- Conduct a simulation experiment
- Determine optimum factors levels
- Calculate the predicted mean
|
|
|
|